In recent years, the United States has been grappling with an alarming housing affordability crisis that threatens the financial stability of countless families. As housing costs skyrocket, many aspiring homeowners find themselves unable to enter the housing market, exacerbating existing homeownership challenges. This upsurge in housing prices can be attributed, in part, to restrictive NIMBY land-use policies that hinder the construction industry’s ability to deliver affordable housing solutions. These regulations not only stifle new development but also prevent innovation, leaving builders struggling to meet the growing demand for homes. As we delve deeper into this pressing issue, it’s essential to understand how these factors interplay to impact the housing landscape.
The current predicament in American housing can be described through various lenses, from escalating property prices to barriers in achieving residential ownership. As communities face pervasive restrictions from local residents, the term ‘NIMBY-ism’ reflects the growing resistance to new housing developments. The diminishing productivity within the construction domain further complicates these homeownership challenges, creating a bottleneck in providing sufficient housing supply. In this context, understanding the implications of regulatory frameworks on the broader housing market becomes crucial, especially in light of rising construction costs and the diminishing returns on investment for builders. Exploring these intricacies not only sheds light on the housing crisis but also offers pathways to potential solutions.
Understanding the Housing Affordability Crisis
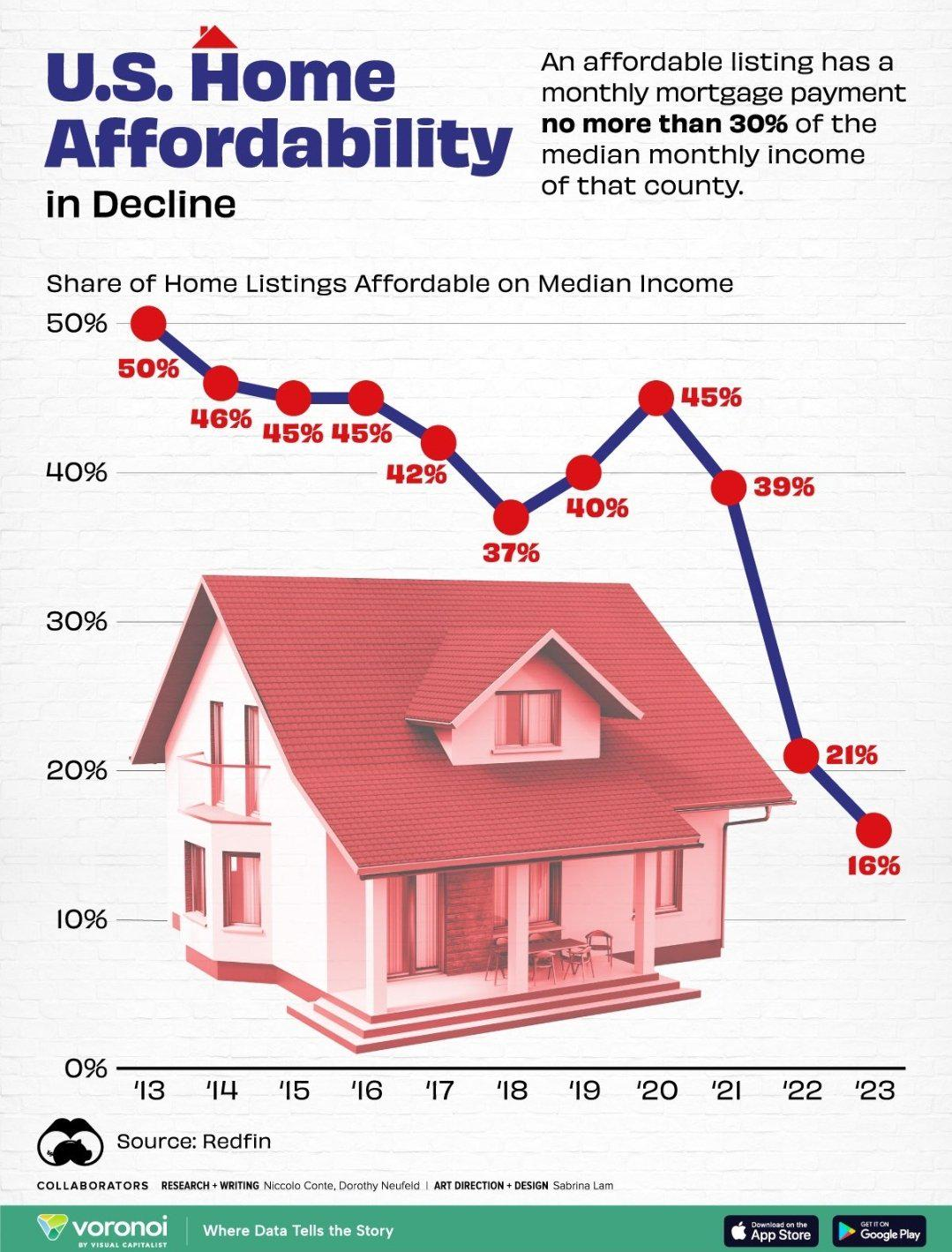
The housing affordability crisis in America has become a pressing issue, highlighting the struggles that many people face in securing homeownership. With housing prices continuing to soar, especially for new single-family homes, countless families find themselves priced out of the market. In fact, research shows that the average price of a new home has more than doubled since 1960, making rent or purchase options less accessible for low and middle-income families. This increase not only reflects heightened demand but also indicates larger systemic issues at play within the housing market.
As affordability dwindles, the American dream of homeownership is at risk. Statistics reveal that younger generations are increasingly unable to afford homes, a trend that can lead to long-term economic consequences. The rising costs of housing, coupled with stagnant wages, accentuate the divide in the market, steering the narrative toward urgent discussions about the sustainability of American housing. Without significant changes in market regulations or a shift in building policies, the housing affordability crisis is set to worsen, calling for innovative solutions and active efforts from policymakers to support prospective homeowners.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the housing affordability crisis and how does it relate to the housing market?
The housing affordability crisis refers to the growing challenge many Americans face in accessing affordable housing, primarily due to escalating housing costs in the housing market. Factors contributing to this issue include rising home prices, stagnant wages, and restrictive NIMBY land-use policies that hinder new construction, limiting options for potential homeowners.
How do NIMBY land-use policies contribute to the housing affordability crisis?
NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) land-use policies contribute to the housing affordability crisis by imposing strict regulations that limit the scale and type of housing developments. These regulations often prevent large-scale projects that could produce affordable housing, stifling innovation and increasing housing costs in the overall housing market.
What are the biggest challenges for homeownership in the current housing market?
Homeownership challenges in the current housing market include rising housing costs, limited inventory due to NIMBY land-use policies, and increasing construction costs. Additionally, many first-time buyers struggle to meet down payment requirements and qualify for mortgages, further complicating the path to homeownership.
What role does the construction industry play in exacerbating the housing affordability crisis?
The construction industry plays a critical role in the housing affordability crisis, particularly through declining productivity and innovation. As NIMBY land-use regulations restrict large-scale housing projects, construction firms have shrunk in size and productivity, leading to fewer homes being built and higher housing costs for consumers.
Why are housing costs rising despite advancements in other industries?
Housing costs are rising due to a combination of stagnant construction productivity and restrictive land-use regulations. While other industries have benefited from mass production and technological advancements, the construction industry has faced declining innovation and increased regulatory barriers, leading to a significant increase in housing costs since the 1960s.
How can we address the housing affordability crisis effectively?
To address the housing affordability crisis, policymakers can consider reducing NIMBY land-use regulations that inhibit large-scale housing developments. Encouraging sustainable construction practices, streamlining permitting processes, and incentivizing affordable housing projects within the construction industry are also vital steps to stabilize housing costs and improve access to homeownership.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Housing Costs | New single-family home prices more than doubled since 1960, largely due to labor and material costs, as well as increased land-use regulations. |
| Impact of NIMBY Policies | Proliferation of ‘not in my backyard’ (NIMBY) land-use regulations has reduced large-scale building projects, leading to higher costs and lower productivity in construction. |
| Decrease in Construction Productivity | Construction productivity fell by 40% between 1970 and 2000, contrasting with continued growth in other industries. |
| Small Builders vs. Large Builders | Large builders produce four times more housing units per employee than smaller firms; however, employment in large construction firms declined after 1973. |
| Generational Wealth Disparity | Wealth accumulation in housing has shifted significantly, with lower middle-aged earners seeing dramatic declines in housing equity from 1983 to 2013. |
Summary
The housing affordability crisis is increasingly prominent as many Americans face the harsh reality of unattainable home ownership. This situation is exacerbated by restrictive land-use regulations that limit builder productivity and innovation, contributing to soaring housing costs—a stark contrast to other sectors where efficiency and scale have improved. As NIMBY sentiments tighten local regulations and build smaller-scale homes, the crisis deepens, creating a cycle that undermines economic mobility and creates generational wealth disparities. Addressing these issues is essential for making housing accessible for future generations.