The housing affordability crisis is a pressing issue that continues to escalate across the United States, leaving many would-be homeowners struggling to find suitable and cost-effective options. In recent decades, escalating real estate regulations and restrictive land-use policies, particularly those driven by NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) sentiment, have significantly constrained the housing market, preventing developers from addressing growing demand effectively. As a result, not only have home prices surged, but the productivity of the construction sector has also taken a hit, further complicating the road to affordable homeownership. With construction productivity declining amidst rising material and labor costs, the challenges faced in the housing market become more daunting. Addressing these issues requires a critical examination of policies that hinder growth and innovation in the construction sector, as they play a pivotal role in the ongoing crisis of homeownership affordability.
The ongoing dilemma of housing affordability has surfaced as one of the most significant economic challenges in contemporary America, often referred to as the housing crisis. This situation is exacerbated by various factors, including NIMBY land-use policies, which restrict the ability of builders to develop expansive housing projects. Additionally, the stagnation in construction productivity highlights a sector struggling to keep pace with rising demand, while stringent real estate regulations impose further barriers to progress. As the costs of homeownership remain out of reach for many, discussions surrounding the need for innovative solutions and policy reform become increasingly urgent. Understanding these elements is crucial for anyone looking to grasp the complexities underlying the current state of the housing market.
The Impact of NIMBY Land-Use Policies on Housing Affordability
The housing affordability crisis in the United States is largely driven by stringent NIMBY land-use policies. These restrictions, while intended to protect neighborhood integrity, often create barriers that prevent the construction of new homes. As various studies have shown, when communities resist changes in zoning laws or new developments, they inadvertently stifle the construction sector’s productivity and innovation. Builders are compelled to adhere to a labyrinth of local regulations, reducing the scale of their projects and increasing overall costs. This not only limits the supply of affordable housing but also significantly escalates the price of existing homes.
Beyond just hindering the supply of new homes, NIMBY policies also discourage large-scale projects that once contributed to affordable housing. Historical data reveals that in the past, significant housing developments were commonplace, allowing builders like Levitt to create large communities at scale. However, with the rise of land-use restrictions, the size of new developments has dramatically shrunk. Today, most housing units are built by smaller firms that, due to their limited capacity, cannot take advantage of the economies of scale necessary for reducing costs. This decline in construction productivity exacerbates the housing affordability crisis, leaving many Americans unable to purchase homes.
Challenges in the Housing Market: Productivity and Regulation
The challenges currently facing the housing market are deeply intertwined with construction productivity and real estate regulations. Since the 1970s, the intersection of increased regulations and declining productivity has created a perfect storm for rising home prices. With builders bogged down by excessive regulatory demands, their capacity to innovate and implement cost-saving techniques diminishes. As a result, the cost of delivering new housing continues to soar, making homeownership increasingly out of reach for average Americans.
Moreover, regulations often inhibit developers from utilizing modern construction methods that could enhance productivity. While industries like manufacturing have seen significant advancements in efficiencies and innovative practices, the construction sector lags behind largely due to these regulatory constraints. Consequently, as out-of-date practices are upheld by city planners and local governments, the gap between housing demand and supply widens, leading to prolonged housing market challenges that further fuel the affordability crisis.
Homeownership Affordability: The Generational Divide
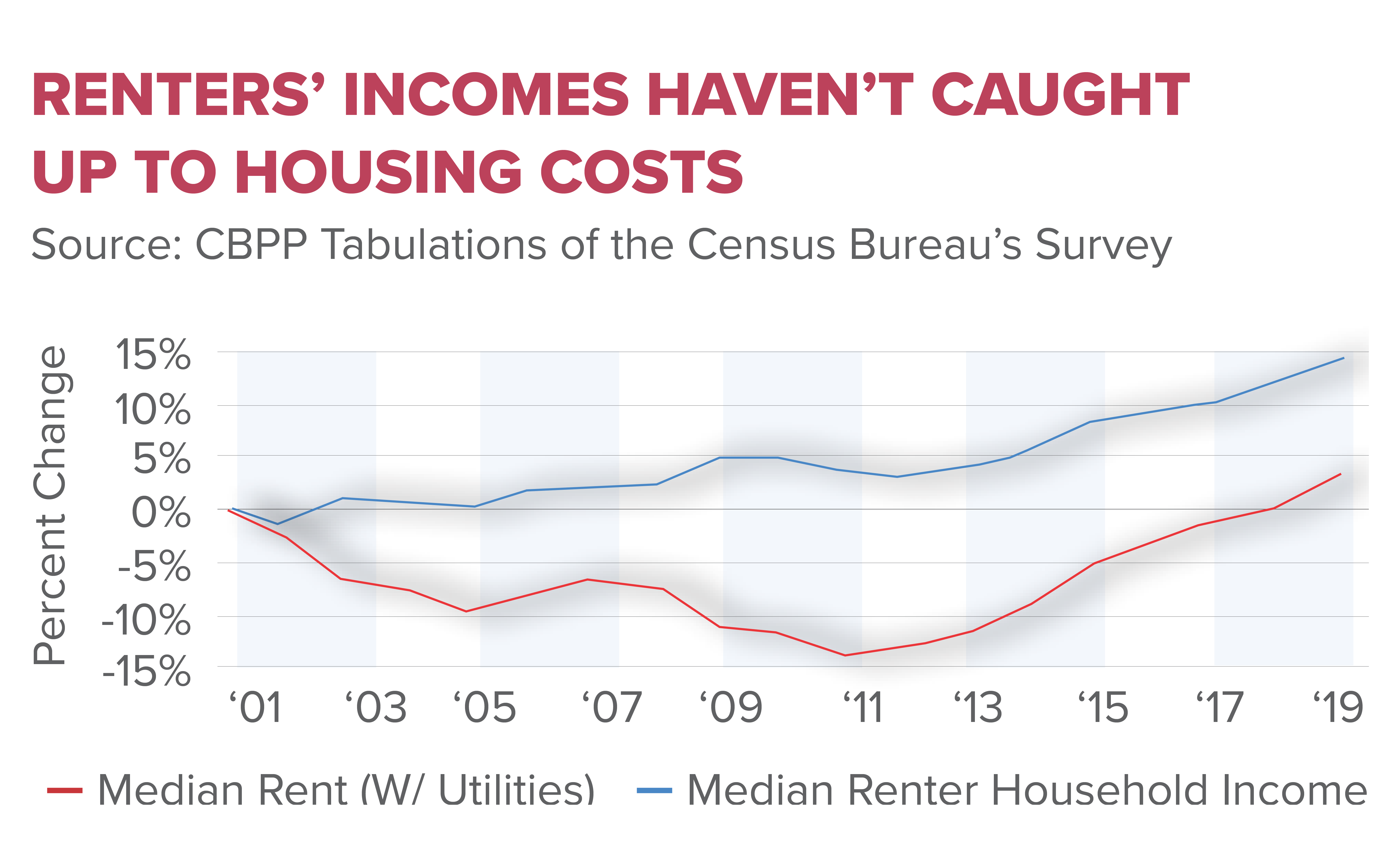
Homeownership affordability has evolved into a pressing issue, revealing stark disparities between generations. As notable research indicates, younger demographics are facing a significant decline in housing wealth compared to older generations. For instance, 35- to 44-year-olds in the U.S. have experienced a dramatic fall in housing equity, with median assets dwindling from $56,000 in 1983 to just $6,000 by 2013. This generational wealth redistribution speaks volumes about the barriers created by the current housing market dynamics influenced by NIMBYism and restrictive land-use policies.
This divide resultantly reshapes the landscape of America’s economic stability. Older generations benefiting from accumulated property wealth are often the ones holding resistance against new developments in their communities. This scenario leads to fewer opportunities for younger generations to enter the looming real estate market, fueling the cycle of rental dependency and limiting the mobility of the labor force. Thus, the rising cost of homeownership, exacerbated by real estate regulations and NIMBY attitudes, not only endangers individual financial stability but also constrains broader economic growth.
Construction Productivity: A Declining Trend
The decline in construction productivity is a concerning trend that has direct implications for housing availability. Amidst the rise of NIMBY land-use policies, builders are confronted with increasing challenges leading to a fallout in productivity levels. Historically, the construction sector boasted the ability to construct vast numbers of homes efficiently, leveraging economies of scale. However, the push for localized planning controls and greater neighborhood input has led to an environment that favors smaller, less productive projects. This shift not only increases costs but also limits the capacity for builders to innovate.
Research indicates that large construction firms produce four times as many housing units per employee compared to their smaller counterparts. The current trend shows that as large builders exit the market, so too does the opportunity for improvements in construction processes. In areas increasingly restrained by NIMBY policies, productivity continues to lag behind other sectors, leading to higher housing prices and reduced homeownership affordability. This trend has sparked urgent calls for reform in construction regulations to encourage larger developments and increased productivity.
Navigating Real Estate Regulations for Housing Solutions
Navigating through the complex labyrinth of real estate regulations has become a significant hurdle for builders looking to address the housing crisis. With various zoning laws and community regulations in place, construction projects can face extensive delays and increased costs that ultimately get passed on to homebuyers. These regulations, often justified by local concerns about density and neighborhood aesthetics, frequently lead to suboptimal housing production solutions that don’t effectively respond to market demands.
However, there is growing recognition that a reassessment of these regulations may be crucial to solving the housing affordability crisis. By streamlining approval processes and revisiting zoning laws, local governments could encourage more efficient project execution and help foster larger developments, which are necessary for addressing housing shortages. Engaging community members in a dialogue about innovative housing solutions may also pave the way for more balanced approaches that consider both community needs and the urgent demand for affordable housing options.
Economic Growth Stifled by Regulating Housing Supply
The paradox of housing regulations lies in their intention to protect neighborhoods while simultaneously stifling economic growth. Housing supply constraints dampen not just individual homeowner prospects but also broader economic development. When communities impose strict land-use controls, they inadvertently slow down job growth and entrepreneurial activity that typically accompany housing expansions. As new industries surface, the lack of affordable housing becomes a considerable impediment as new employees seek residence in these burgeoning areas.
Furthermore, the economic implications of constrained housing supply extend to various sectors. With fewer available homes, employees may find themselves commuting longer distances or even relocating out of state, leading to labor shortages in critical areas. For a robust economic landscape, it is vital to reconcile community preferences with the pressing need for housing. Engaging community stakeholders and recalibrating regulatory frameworks can help spur the construction of new homes and ultimately fuel economic growth.
Evaluating Construction Investment Against Housing Demands
Evaluating construction investment amid rising housing demands presents both a challenge and an opportunity for the economy. The disconnect between investment in construction and the acute need for affordable housing often results from the inhibitive nature of local real estate regulations. Investors are often hesitant to commit to projects overshadowed by the uncertainties posed by heightened regulatory scrutiny and lengthy approval processes. Consequently, potential developments that could significantly alleviate the housing affordability crisis remain stalled.
Encouraging higher rates of investment in construction requires a collective effort to address regulatory burdens. Streamlining the approval process and simplifying zoning laws can create a more attractive environment for lenders and developers alike. By fostering collaborative relationships with local authorities, builders can effectively mitigate risks and invest in projects that not only expand construction output but also cater to the surging housing demand.
The Future of Homeownership in an Evolving Market
As the housing market continues to evolve, the future of homeownership hangs in a precarious balance amid rising prices and regulatory challenges. The persistent housing affordability crisis faced by many Americans signals an urgent need for actionable solutions that prioritize accessible homeownership. While innovative construction techniques and financial products may reduce entry barriers, the real game-changer lies in supportive policies that encourage sustainable housing development.
Looking ahead, the potential for intergenerational wealth transfer hinges on the ability to create inclusive homeownership strategies. By promoting fair lending practices alongside policies that encourage the development of affordable housing, younger generations can regain a foothold in the real estate market. Community engagement in these efforts is paramount to ensure that new housing developments not only address the current crisis but are also sustainable for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main contributors to the housing affordability crisis in the U.S.?
The housing affordability crisis in the U.S. is primarily driven by factors such as rising labor and material costs, stringent real estate regulations, and NIMBY land-use policies that restrict new developments. These factors limit construction productivity and contribute to soaring home prices, making homeownership increasingly unattainable for many Americans.
How do NIMBY land-use policies exacerbate the housing affordability crisis?
NIMBY land-use policies exacerbate the housing affordability crisis by limiting the type and scope of housing developments. These policies create barriers that require extensive approvals and micromanagement, resulting in smaller, bespoke projects that fail to benefit from the cost efficiencies of mass production. This reduction in construction productivity leads to higher home prices, further straining affordable homeownership.
What role do real estate regulations play in housing market challenges?
Real estate regulations significantly impact housing market challenges by imposing restrictions that can stifle construction and innovation. Tighter regulations can inhibit new housing supply and increase costs for builders. Consequently, these challenges contribute to the ongoing housing affordability crisis, making it difficult for potential homeowners to find affordable housing options.
How has construction productivity influenced homeownership affordability?
Construction productivity has a direct influence on homeownership affordability. Over the decades, declining productivity in construction, largely due to restrictive land-use policies, has resulted in fewer housing units being built relative to demand. As the supply of homes fails to keep pace with rising demand, homeownership becomes less affordable for a growing segment of the population.
What is the impact of rising home prices on young buyers facing the housing affordability crisis?
Rising home prices disproportionately affect young buyers, exacerbating the housing affordability crisis. As prices continue to increase, many young adults find homeownership out of reach, leading to significant intergenerational wealth transfers where older homeowners benefit while younger generations struggle to enter the housing market.
How can policymakers address the housing affordability crisis related to construction productivity?
Policymakers can address the housing affordability crisis by reforming NIMBY land-use policies and streamlining real estate regulations to encourage larger-scale housing projects. By promoting policies that enhance construction productivity and reduce barriers to development, more affordable housing options can be created, alleviating the strain on potential homeowners.
Why is homeownership becoming increasingly unattainable in today’s housing market?
Homeownership is becoming increasingly unattainable due to a combination of factors, including escalated costs of new construction, restrictive real estate regulations, and stagnant wages. Additionally, a decline in construction productivity, attributed to NIMBY policies, has reduced the availability of affordable housing, making it difficult for many to achieve homeownership.
| Key Points |
|---|
| The U.S. is experiencing a housing affordability crisis, with ownership becoming increasingly unattainable for many Americans. |
| The price of new single-family homes has more than doubled since 1960, driven by various factors including labor and material costs, as well as regulatory impacts. |
| NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) land-use policies have hindered builders, resulting in smaller projects with less innovation and productivity. |
| Research shows that the construction sector’s productivity peaked between 1935 and 1970 but has declined by 40% since, influenced by escalating land-use regulations. |
| Large-scale constructions, like those seen in Levittown, have nearly vanished, significantly impacting housing supply and costs. |
| The intergenerational transfer of housing wealth has intensified, with younger generations holding significantly less equity compared to older demographics. |
Summary
The housing affordability crisis is a pressing issue that has developed due to a combination of rising home prices, regulatory barriers, and diminishing productivity in the construction sector. As the cost of new homes continues to escalate, many Americans find themselves unable to enter the housing market. The stifling effect of NIMBYism has contributed to the decline of large-scale developments, which historically offered economies of scale that made housing more accessible. Without substantial changes to land-use policies and a focus on increasing construction innovation, the situation is unlikely to improve, further entrenching economic inequalities across generations.