Liberal arts education plays a pivotal role in shaping well-rounded individuals capable of critical thinking and adaptive problem-solving. In a rapidly changing job market, the importance of liberal arts has come under scrutiny, yet its value remains significant as it equips students with essential skills that transcend specific professional fields. From fostering creativity and analytical abilities to enhancing communication proficiency, a liberal arts education prepares graduates to thrive in diverse environments. Critics, however, question its relevance in a world increasingly driven by vocational training, prompting discussions on the future of liberal arts education. As we navigate these challenges, understanding the return on investment in a liberal arts education becomes critical to ensuring its continued presence and support in academic institutions.
A humanities-focused education, often referred to as liberal arts schooling, encompasses a broad spectrum of disciplines that promote intellectual flexibility. This educational approach, which emphasizes the development of critical thought and effective communication, is crucial for individuals aiming to stand out in various career paths. The growing trend among students to pursue more specialized, vocational training has led to increased debate regarding the value of a humanities-centric curriculum. Despite criticisms surrounding its practical applicability in today’s job market, the benefits offered by a humanities education, such as fostering a deep understanding of societal dynamics and equipping students with transferable skills, cannot be overlooked. As we consider the trajectory of higher education, re-evaluating and enhancing this approach may prove vital for cultivating adaptable leaders in an ever-evolving economy.
The Essential Value of a Liberal Arts Education
A liberal arts education is often seen as a broad pathway, encompassing disciplines such as humanities, arts, and social sciences. Its essential value lies in fostering critical thinking, creativity, and adaptability. In today’s rapidly changing job market, employers are increasingly looking for individuals who can think independently and solve complex problems—skills that are at the core of a liberal arts curriculum. As noted by educators like David Deming, a well-executed liberal arts education doesn’t just cluster knowledge in specific fields; rather, it equips students with versatile tools that prepare them for unforeseen challenges, allowing them to navigate an evolving economy with ease.
Moreover, the importance of a liberal arts education extends beyond the workplace. It cultivates informed citizens, capable of engaging in meaningful discourse, which is vital for maintaining a democratic society. Critics argue that liberal arts are less valuable in terms of immediate job prospects compared to vocational training, yet this perspective overlooks the long-term benefits of developing well-rounded individuals who can navigate a complex world. The skills acquired through a liberal arts education—effective communication, analytical thinking, and ethical reasoning—are invaluable, transcending specific job roles and enhancing personal growth.
Addressing the Criticism of Liberal Arts
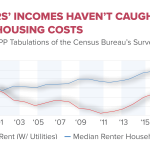
While the criticisms surrounding liberal arts education have grown, especially regarding its job market relevance, it is essential to unpack these arguments thoughtfully. Many argue that a liberal arts degree does not lead to stable employment, especially in a financially driven economy that pushes for immediate returns on educational investments. However, figures show that, although liberal arts graduates may start with lower wages, they often see their salaries rise considerably over time, contradicting the perception that vocational training alone guarantees financial success.
Furthermore, discussions about the liberal arts often ignore the socio-economic barriers that restrict first-generation students and those from low-income backgrounds from pursuing such educational paths. Nancy Hill points out that many people perceive liberal arts education as a luxury, which alienates those who may benefit from diverse educational experiences. This misrepresentation hampers enrollment and ultimately denies society a broader base of innovative thinkers and leaders who are essential for driving cultural and economic progress.
The Future of Liberal Arts Education
Looking forward, the future of liberal arts education hinges on its ability to adapt to the changing job market and societal needs. As noted in conversations among educators, integrating liberal arts with vocational training can provide a comprehensive educational experience that addresses both breadth and depth. By encouraging project-based learning that emphasizes real-world applications, universities can make liberal arts more attractive to students who prioritize job readiness.
In addition, the ongoing dialogue about the role of technology in education presents new opportunities for liberal arts institutions. By embracing digital tools and innovative teaching methods, educators can engage students in a more interactive and meaningful way. This shift not only enhances the learning experience but also prepares graduates to thrive in a tech-driven economy where creativity and adaptability are paramount.
Navigating Economic Realities in Education
Today’s economic landscape dramatically impacts students’ perceptions of the value of higher education, particularly liberal arts. With rising tuition costs and growing concerns about debt, many families find themselves questioning the return on investment of a college education. As noted in the podcast, the ongoing societal narrative often prioritizes immediate skills over a well-rounded education, leading to declining enrollments in liberal arts programs.
However, as educators assert, a liberal arts education not only prepares students for a range of jobs but also enhances their overall capabilities and well-being. Emphasizing the importance of critical thinking and adaptability, liberal arts graduates often find themselves better equipped for fluctuating job markets and diverse career paths. This enduring relevance of liberal arts in a tense economic climate reinforces its value as not just an academic choice, but a life-long asset.
Enhancing Accessibility in Liberal Arts
One of the key issues confronting liberal arts education today is accessibility. As many educators, including Nancy Hill, have pointed out, the perception of liberal arts as a luxury often prevents underprivileged students from exploring this educational pathway. To counteract this issue, institutions must innovate and find ways to create supportive environments that empower students from all backgrounds to pursue liberal arts degrees.
Initiatives that provide financial aid, mentorship, and flexible course offerings are essential for attracting diverse student populations to liberal arts programs. Opening up these opportunities not only benefits the individuals involved but also enriches the academic environment by fostering a wider array of perspectives and ideas. By leveling the playing field, schools can help students find confidence and inspiration in exploring the expansive world of liberal arts.
Liberal Arts as a Catalyst for Civic Engagement
A liberal arts education plays a pivotal role in preparing students for active participation in civic life. As political and social challenges become increasingly complex, the ability to engage in critical discourse and cultural dialogue is crucial. Educators like Susanna Siegel highlight that fostering a strong foundation in liberal arts nurtures the skills needed to navigate diverse opinions and collaborate with varying perspectives.
By centering liberal arts in educational institutions, we lay the groundwork for a socially aware citizenry capable of problem-solving and ethical reasoning. The connection between education, literacy, and democratic engagement is well-established, and as such, promoting liberal arts is not merely an academic choice but a necessity for cultivating informed and engaged communities.
The Role of Technology in Liberal Arts Education
The rise of technology within educational practices poses new opportunities and challenges for liberal arts disciplines. Educators must now consider how to effectively integrate digital tools and innovative teaching methods into their curricula. This transition presents an exciting chance to enhance student engagement and comprehension while also addressing contemporary challenges in education, such as those posed by online learning environments.
Liberal arts can lead the charge in developing comprehensive curricula that leverage technology for collaborative and project-oriented assignments. By moving away from traditional, passive learning models, educators can encourage a more participative and hands-on approach, vital in developing critical thinking skills that are essential for today’s workforce. This not only enriches the learning experience but also ensures that graduating students are prepared to thrive in an increasingly digital world.
Reevaluating Perceptions of Liberal Arts
As skepticism surrounding the value of higher education continues to grow, particularly against the backdrop of rising costs and economic challenges, it’s crucial to reevaluate the perceptions of liberal arts programs. Many families still regard these degrees as less lucrative compared to STEM fields; however, the long-term benefits of a liberal arts education extend far beyond immediate financial returns. Graduates often possess exceptional communication skills, creativity, and analytical abilities that set them apart in the job market.
Reframing the conversation around liberal arts education to highlight its broader impacts—such as the development of well-rounded individuals who can adapt to various challenges—will be vital for its future. As industries evolve, the demand for agile thinkers and innovative problem-solvers will only increase, underscoring the importance of a liberal arts education in preparing students for unanticipated career paths.
Creating Interdisciplinary Pathways in Education
One promising approach to revitalizing liberal arts education is fostering interdisciplinary pathways that combine traditional liberal arts disciplines with vocational training. By cultivating educational experiences that meld subjects such as philosophy, history, and literature with skills in technology or business, universities can create a more appealing, holistic approach to education. This model not only enhances student engagement but also prepares graduates to meet complex demands in diverse job markets.
Encouraging collaboration between different fields fosters a culture of creativity and innovation that is essential in the modern job landscape. As industries become increasingly interconnected, a liberal arts foundation paired with practical skills will equip graduates with the adaptability and problem-solving capabilities necessary to succeed, paving the way for new opportunities and applications beyond traditional career paths.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the importance of liberal arts education in today’s society?
The importance of liberal arts education lies in its ability to cultivate critical thinking, creativity, and the capacity for independent thought, which are essential for active participation in a democratic society. It prepares students to tackle complex problems and adapt to changing job markets, providing them with versatile skills applicable across various fields.
How does a liberal arts education add value in the job market?
A liberal arts education adds value in the job market by equipping graduates with strong communication, analytical, and problem-solving skills. Employers often seek individuals who can think critically and adapt to new challenges, making liberal arts graduates attractive candidates for a diverse range of roles beyond specific vocational training.
What are some common criticisms of liberal arts education?
Common criticisms of liberal arts education suggest it is overly broad and lacks direct job training, leading some to view it as less practical compared to specialized degrees. Critics argue that this absence of specific skill training may result in lower initial earning potential for graduates.
What is the future of liberal arts education in an evolving job market?
The future of liberal arts education appears promising as the job market increasingly values adaptable skills over narrow expertise. With automation and industry changes, a liberal arts education offers a foundation for lifelong learning and adaptability, essential traits as workers navigate shifting career landscapes.
Why might some perceive liberal arts education as a luxury?
Many perceive liberal arts education as a luxury due to the rising costs of college tuition and the economic pressures faced by prospective students. The view that practical vocational training is more valuable can diminish the perceived accessibility and relevance of liberal arts in today’s economy.
How can institutions make liberal arts education more appealing to students?
Institutions can make liberal arts education more appealing by demonstrating its real-world applications, integrating experiential learning opportunities, and showcasing how liberal arts skills align with career readiness. Enhancing financial aid offerings and reducing costs can also broaden access to these programs.
What role does liberal arts education play in fostering democratic citizenship?
Liberal arts education plays a crucial role in fostering democratic citizenship by promoting critical thinking, ethical reasoning, and the ability to engage in diverse viewpoints, which are foundational for informed and responsible participation in democratic processes and community life.
How does liberal arts education contribute to mental health and well-being?
Liberal arts education contributes to mental health and well-being by encouraging self-discovery, community engagement, and open dialogue about diverse perspectives. This exposure helps students develop resilience and emotional intelligence, skills vital for navigating personal and professional challenges.
Can a liberal arts education lead to successful careers?
Yes, a liberal arts education can lead to successful careers, as graduates often find fulfillment in diverse fields such as education, healthcare, public policy, and creative industries. Many liberal arts majors report higher job satisfaction and adaptability throughout their careers despite initial income disparities.
What skills do students gain from a liberal arts education that are beneficial in the workplace?
Students gain essential skills from a liberal arts education, such as critical thinking, effective communication, collaboration, and cultural awareness. These skills enhance their ability to work in teams, solve complex problems, and navigate various workplace dynamics, making liberal arts graduates valuable to employers.
| Key Points | Description |
|---|---|
| Importance of Liberal Arts Education | Liberal arts education fosters critical thinking, creativity, and adaptability, preparing students for diverse job markets. |
| Critique of Perception | Some view liberal arts as a luxury rather than a fundamental education, affecting accessibility for low-income students. |
| Long-term Benefits | Liberal arts majors may earn less initially but have the potential to catch up in earnings over their careers. |
| Adaptation to Job Market | As job markets change, there is an increased emphasis on specific qualifications, yet liberal arts skills remain valuable. |
Summary
Liberal arts education plays a crucial role in developing critical and independent thinking among students, vital for both personal growth and democratic society. It equips learners with a diverse skill set that transcends specific fields, enabling them to adapt in an ever-evolving job market. Despite critiques viewing liberal arts as less practical, this form of education nurtures creativity, cultural understanding, and intellectual flexibility, preparing graduates for a range of challenges in the workforce and society. Emphasizing accessibility and perceived value can help reshape the conversation around liberal arts education, ensuring it remains a cornerstone of higher education.